
This result indicates that XYZ Corp has $3.00 of debt for every dollar of equity. Banks also tend to have a lot of fixed assets in the form of nationwide branch locations. The other important context here is that utility companies are often natural monopolies. As a result, there’s little chance the company 5 necessary management traits of operations leaders will be displaced by a competitor. They may note that the company has a high D/E ratio and conclude that the risk is too high. For this reason, it’s important to understand the norms for the industries you’re looking to invest in, and, as above, dig into the larger context when assessing the D/E ratio.
Debt Equity Ratio Template
This ratio compares a company’s equity to its assets, showing how much of the company’s assets are funded by equity. If earnings don’t outpace the debt’s cost, then shareholders may lose and stock prices may fall. The debt-to-equity ratio can clue investors in on how stock prices may move. As a measure of leverage, debt-to-equity can show how aggressively a company is using debt to fund its growth. A debt-to-equity-ratio that’s high compared to others in a company’s given industry may indicate that that company is overleveraged and in a precarious position.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio Frequently Asked Questions
The D/E ratio indicates how reliant a company is on debt to finance its operations. They do so because they consider this kind of debt to be riskier than short-term debt, which must be repaid in one year or less and is often less expensive than long-term debt. And, when analyzing a company’s debt, you would also want to consider how mature the debt is as well as cash flow relative to interest payment expenses. Additional factors to take into consideration include a company’s access to capital and why they may want to use debt versus equity for financing, such as for tax incentives.
Company
In contrast, a company with a low ratio is more conservative, which might be more suitable for its industry or stage of development. Considering the company’s context and specific circumstances when interpreting this ratio is essential, which brings us to the next question. Sectors requiring heavy capital investment, such as industrials and utilities, generally have higher D/E ratios than service-based industries.
- The debt-to-equity ratio (D/E) is one of many financial metrics that helps investors determine potential risks when looking to invest in certain stocks.
- In this case, any losses will be compounded down and the company may not be able to service its debt.
- Therefore, it is essential to align the ratio with the industry averages and the company’s financial strategy.
✝ To check the rates and terms you may qualify for, SoFi conducts a soft credit pull that will not affect your credit score. Finally, the debt-to-equity ratio does not take into account when a debt is due. A debt due in the near term could have an outsized effect on the debt-to-equity ratio. So in the case of deciding whether to invest in IPO stock, it’s important for investors to consider debt when deciding whether they want to buy IPO stock. However, because the company only spent $50,000 of their own money, the return on investment will be 60% ($30,000 / $50,000 x 100%).
A company’s total debt is the sum of short-term debt, long-term debt, and other fixed payment obligations (such as capital leases) of a business that are incurred while under normal operating cycles. Changes in long-term debt and assets tend to affect the D/E ratio the most because the numbers involved tend to be larger than for short-term debt and short-term assets. If investors want to evaluate a company’s short-term leverage and its ability to meet debt obligations that must be paid over a year or less, they can use other ratios. A lower debt-to-equity ratio means that investors (stockholders) fund more of the company’s assets than creditors (e.g., bank loans) do. It is usually preferred by prospective investors because a low D/E ratio usually indicates a financially stable, well-performing business. The D/E ratio is a powerful indicator of a company’s financial stability and risk profile.
A high debt to equity ratio means that a company is highly dependent on debt to finance its growth. Calculate debt-to-equity ratio of a business which has total liabilities of $3,423,000 and shareholders’ equity of $5,493,000. If the debt to equity ratio gets too high, the cost of borrowing will skyrocket, as will the cost of equity, and the company’s WACC will get extremely high, driving down its share price. As a rule, short-term debt tends to be cheaper than long-term debt and is less sensitive to shifts in interest rates, meaning that the second company’s interest expense and cost of capital are likely higher. If interest rates are higher when the long-term debt comes due and needs to be refinanced, then interest expense will rise.
This means that for every dollar in equity, the firm has 42 cents in leverage. A ratio of 1 would imply that creditors and investors are on equal footing in the company’s assets. The debt-to-equity ratio is the most important financial ratio and is used as a standard for judging a company’s financial strength. When examining the health of a company, it is critical to pay attention to the debt-to-equity ratio. If the ratio is rising, the company is being financed by creditors rather than from its own financial sources, which can be a dangerous trend. Lenders and investors usually prefer low debt-to-equity ratios because their interests are better protected in the event of a business decline.
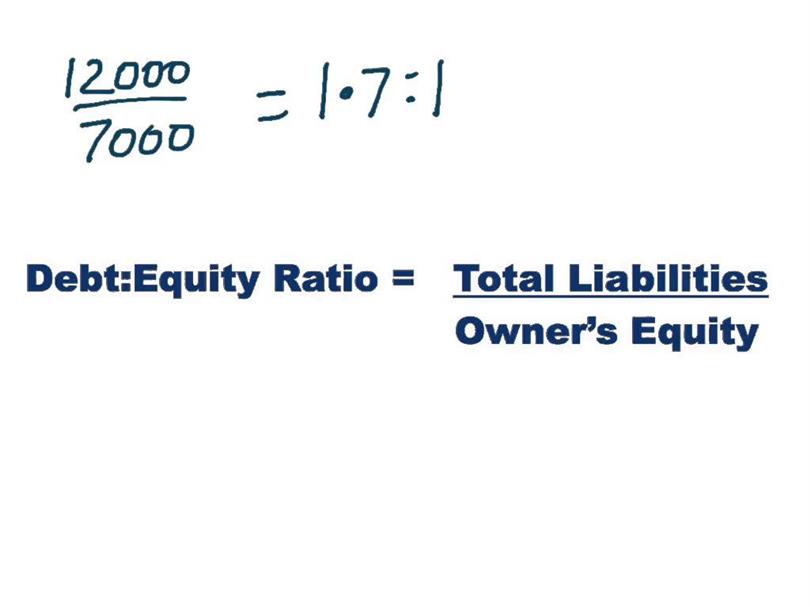
But it can also show investors that business owners aren’t realising their company’s full potential because they’re not borrowing to grow. Your company’s equity is the total value of its assets, after deducting liabilities. Understanding the average Debt to Equity ratio in your industry helps contextualize your company’s financial standing. This comparison can inform strategic decisions regarding financing and growth. Companies can manage their Debt to Equity ratio by controlling debt levels and increasing equity through retained earnings or issuing new shares.
11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements. 11 Financial’s website is limited to the dissemination of general information pertaining to its advisory services, together with access to additional investment-related information, publications, and links. However, an ideal D/E ratio varies depending on the nature of the business and its industry because there are some industries that are more capital-intensive than others. The quick ratio is also a more conservative estimate of how liquid a company is and is considered to be a true indicator of short-term cash capabilities.
It is possible that the debt-to-equity ratio may be considered too low, as well, which is an indicator that a company is relying too heavily on its own equity to fund operations. In that case, investors may worry that the company isn’t taking advantage of potential growth opportunities. Companies that don’t need a lot of debt to operate may have debt-to-equity ratios below 1.0. The debt-to-equity ratio (D/E) is one of many financial metrics that helps investors determine potential risks when looking to invest in certain stocks. However, such a low debt to equity ratio also shows that Company C is not taking advantage of the benefits of financial leverage. An increasing trend in of debt-to-equity ratio is also alarming because it means that the percentage of assets of a business which are financed by the debts is increasing.
